Essential tools: high-speed steel end mills, lathe tools, workholding devices, calipers, coolant systems. Ensure precision, reduce heat, improve CNC machining efficiency
CNC milling cutter
Selection
-
The selection of the CNC milling cutters in the key to efficient machining.
-
Important factors include material, coating and geometry.
-
High-speed steel and carbide cutters are the most widely used because of their durability. The exact type of cutter to be used should be considered based on the specific task details.
-
Titanium nitride coating increases the service life of the CNC milling cutters and reduces the wear. There are various reasons behind the use of the given coating.
Types
The selection of CNC milling cutters largely depends on the task.
-
End mills are probably the most frequently used because of the wide range of operations that they can perform.
-
For 3D contouring and for making parts with the complex shape ball nose cutters are ideal.
-
For making parts that will later be machined in the additional way corner radius end mills are preferred as they reduce the wear of the cutter and improve the surface finish.
-
For high-efficiency surface milling face mills are the best option.
Real-world example
-
A precision engineering firm made aerospace components with the help of the ball nose cutters. Tolerances of 0.01 mm have been successfully achieved.
Materials
Different materials have different beneficial characteristics.
-
High-speed steel cutters are durable although they are not hard. They are cost-effective and are perfect for softer materials like aluminum. In the automotive industry, these cutters are used for fast machining of steel parts.
-
Carbide cutters are much harder and can be used in all projects that HSS cutters are used. They are ideal for the automotive industry because of their ability to maintain the sharpness and ability to provide high-speed operations. Ceramic cutters are harder but more brittle. They are used in high-temperature applications.
-
In the automotive industry, valves and springs are made with the help of the carbide cutters.
Coatings
-
The coatings also prolong the lifespan of the CNC milling cutters and improve their characteristics.
-
Titanium nitride increases the hardness of the cutter and reduces the friction.
-
Titanium aluminum nitride embedding ensures excellent heat resistance. There are other reasons behind the use of the given coating.
-
Diamond coatings help to mill the non-ferrous materials and composites. In the automotive industry, stainless steel parts are milled. A manufacturer switched to TiAlN-coated cutters and the cost savings amounted to 50%.
Maintenance
-
Regular cleaning up is required. Otherwise, debris will form a protective layer and the milling will not take place.
-
Sharpening and the regular inspection are required as well. Otherwise, the cutting might be either impossible or dangerous.
Applications
-
The given applications depend largely on the industry.
-
Aerospace components must be either light or heavy and as small as possible. No materials that could provide adequate characteristics must be used.
-
In the automotive industry, precision is not so important and parts must be heavy and strong. In the medical industry, the parts must be light and modern equipment with the precise characteristics can be used.
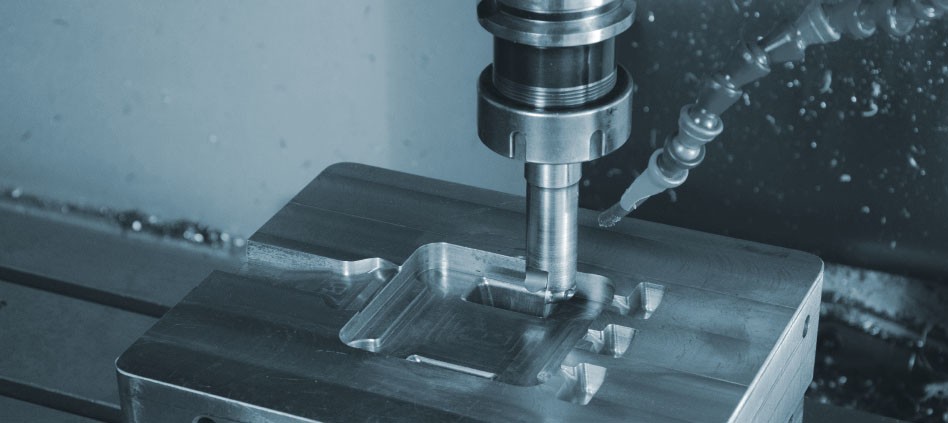

CNC turning tool
Choosing the right CNC turning tool is the first step in achieving precise results and prolonging the life of the cutting instrument. It is determined by the material, tool geometry, and coating. Among the cutting materials, carbide inserts are the most popular due to their hardness and resistance to heat. In terms of geometry, a replaceable insert’s nose radius determines the quality of the surface finish and chip formation. For instance, a CNC lathe with a milling spindle and tool holder could have a 0.8mm nose radius, improving the surface finish of stainless steel to Ra 0.4 µm. While turning stainless steel at high speeds, a CVD coating is used to enhance the wear resistance. There are several types of CNC turning tools, including finishing ones, which produce a very fine finish; roughing tools, which remove a large amount of material, and parting and grooving tools.
Typical Uses
Roughing tools are used to remove large pieces of material quickly. For example, a manufacturing shop recently employed a roughing tool with a large nose radius to rapidly remove material from a titanium billet, and its cycle time dropped significantly. While finishing these tools, a finishing running tool is needed to achieve a fine surface finish. Among the other turning tools, they include parting tools, which eradicate an additively-manufactured component from a large billet, as well as grooving tools, which produce certain grooves and recesses. Different tasks call for different CNC turning tools. The performance of turning tools depends on their material:
Carbide: It is highly hard and thermal-resistant and well-suited for hard materials
HSS: It is an inferior solution, but it is cheaper and can cut softer materials
Ceramic and cermet: They are well-suited for high speeds and heating temperatures
Are some materials best suited for certain applications
For example, ceramic turning tool inserts are employed in the aerospace industry to turn cast and nickel-based superalloys. These tools performed well at high temperatures and allowed tool cutting edges to remain well engineered and razor-sharp. Some of the most common coatings for CNC turning tools are TiN, which covers a carbide turning insert in this image, and Al2O3. They boosted the tool’s life expectancy by 30% while turning hardened steel in the shop. The machining process was also considerably enhanced.
Maintenance of the CNC Turning Tools
It encourages outstanding cutting performance and many years of cutting tool use. Firstly, chips and other pollutants must be removed on a regular basis. This is particularly important at the stage of replacing inserts. In addition, it is also crucial to test the tool for wear and other damage as regularly as possible. The measurement of cutting tools must be executed with certain instruments with precision, and, if required, the tools must be immediately replaced. Finally, cutting tools should be sharpened regularly to ensure their precise and fast cutting. It is noteworthy that cutting equipment may well behave normally even at rough machining if all of the aforementioned checks are successfully passed. To summarise the information above, many of the turning tools are used for specific purposes. It may be roughing or finishing tool, parting or grooving tool. Alternatively, the turning tool’s properties are comprised of the material it is made of. They vary from carbide to ceramic. A common type of ceramic used for tools is a syalon that consists of silicon nitride and has reasonable properties. In fact, coatings are also crucial because of the benefits they trigger. A well-coated tool may experience 30% more years of use. In addition, combination tools experience the qualities of all of the materials they are composed of.
Fixtures and Tooling
Fixtures
A fixture is a clamping and holding device used in CNC machining to secure the workpiece firmly. Fixtures guarantee precision, repeatability, and safety. A well-designed fixture minimizes the workpiece’s movement, which reduces the occurrence of errors and improves the surface finish. For instance, aerospace manufacturers use custom fixtures to ensure they maintain ±0.002mm tolerance in their complex component machining. The fixture types include:
-
Vise fixtures – used to secure the smaller objects
-
Clamping fixtures – holds the irregular shaped objects
-
Modular fixtures – effective systems that can be reconfigured for many tasks
-
Dedicated fixtures – used for one type of object, which ensures the best possible accuracy and efficiency
In an automotive plant, dedicated fixtures are used when machining engine blocks. This ensures that each engine block is held the same way and results in a uniform quality of the output.
Some of the most important considerations in fixture design include:
-
Material: steel or anodized aluminum for strength and durability
-
Positioning: precise positioning pins and locators to ensure repeatability
-
Clamping force: enough force to prevent movement without deforming the workpiece
-
Ease of use: quick-change fixture designs reduce the setup time
For example, a medical device company was able to save 40% of the time needed for the setup and subsequently reaching a 50% throughput increase by designing a fixture that had precision-ground steel locators and quick-release clamps.
Tooling
Tooling refers to the cutting tools and accessories in which a CNC machine may be equipped. Selection of the proper tooling directly affects the efficiency of machining, surface finish, and the life of the toolings. In CNC machining, carbide and high-speed steel tools are often used due to increased durability and performance. There are many tooling types, most important of which are:
End Mills: Machining slots, profiles, and contours.
Drills: Making holes to extremely high levels of precision.
Reamers: Ensuring tight tolerances and a good finish on holes.
Taps and Dies: Cutting threads.
For instance, one precision engineering company made use of carbide end mills to machine hardened steel molds. Their precision was so high they could achieve a tolerance of ±0.01 mm, along with a very good surface finish.
-
Maintaining fixtures and tooling
Cleaning: Chips and other debris should be removed from fixtures and tooling after each operation and not allowed to accumulate.
Inspection: Regular inspections and diagnostics should be run in order to determine if fixtures and tooling are wearing or failing. This is not just for the sake of maximizing efficiency but also to prevent damage and waste caused by faulty machining.
Calibration: A fixture or tooling that is slightly out of tolerance may be causing mistakes to occur.
Tip: A good way to maintain high standards of quality and acceptability in fixtures and tooling is to run a preventative maintenance schedule. This avoids the sudden, unexpected breakdown of equipment.
-
Applications of fixtures and tooling
Fixtures and tooling are used in a wide range of industries:
Aerospace: Machines complex components at extreme levels of precision.
Auto: Makes highly accurate parts such as engine parts.
Medical: Produces extremely accurate items like surgical instruments and implants.
For example, it is necessary in the aerospace industry to use custom fixtures and special tooling to machine turbine blades. Each blade is designed to standards of aerodynamics and structural integrity.
-
Innovations in fixtures and tooling
Several recent advances have been made that have improved fixtures and tooling, allowing for greater precision and time savings:
Additive Manufacturing: Allows complex, custom fixtures to be produced rapidly.
Smart Tooling: Uses sensors to monitor the health of tooling in real time.
Advanced Materials: New materials like composites and ceramics are used to improve tooling performance.

Measuring Tools
Why Measuring Tools are Important
Measuring tools are indispensable in CNC manufacturing. They help to ensure that produced parts are dimensionally accurate and produced within tolerance ranges. Measurement is particularly important in high-precision CNC machining, such in the aerospace and medical industries. The tools help to ensure that gear pitch, threads, form cutters, and all other dimensions are perfectly measured. This is especially crucial in the aerospace industry as the smallest difference in measurement can have devastating implications. Measuring tools that are used in CNC machining
Different types and makes of tools can be used for measuring in the CNC machining industry. These include:
- Calipers. These are the most popular and versatile tools used in the industry. They can be used to measure internal, external, and depth dimensions. Digital calipers give new and accurate figures of ±0.01 mm.
- Micrometers. They offer a precise way to measure thickness and diameter. Normally, in these tools, their resolution is as high as ±0.001 mm.
- Dial indicators. These are used to measure small displacements and abnormalities of any form of setup of parts. They are also used in inspections.
- Height gauges. These are used to measure heights and distances in a vertical direction. Heights gauges are essential in ensuring part uniformity is achieved.
Real-world application
For example, a machine shop was given a contract to manufacture various parts of an orthopedic kit for young children. The parts had to be delivered within a week. To verify that the parts are produced within the required tolerance range of ±0.02 mm, the company uses digital calipers to check it.. In this case, the closing of the clamp at zero indicates maximum tolerance limit. Another real-world application can be found in the automotive industry where micrometers of resolution of a ±0.001 mm is used to measure engine pistons. The size of the piston largely influences the power of the engine.
Calibration and Maintenance of Measuring Tools
Accuracy of measuring tools is maintained by regular calibration and proper care. As such, the following tips can be provided:
Calibration. Regular calibration of the tools against certified standards will help to maintain their accuracy. It is worth noting that calipers as well as micrometers should be at least annually calibrated. One should mention that they need to be specifically calibrated by experts.
- Cleaning. Tools should be clean and free of any debris.
- Storage. Tools should be stored in protective cases.
Tip: In order to ensure that all measuring tools are calibrated and do not introduce an undue risk for inaccurate measuring process, a schedule should be invented. At the same time, written records also should be maintained. Applications of Measuring Tools
Measuring tools are used in the following applications:
- Setup. Dial indicators as well as height gauges are used to ensure the workpiece is positioned correctly on the machine. In-process inspection. At this stage, calipers together will micrometers are used to check dimensions. The purpose is to guarantee that the part remains within tolerances determined by the blueprint.
- Final inspection. At the final inspection, a vast amount of measuring tools are used to ensure that a part about to be shipped meets all the necessary requirements.
- In the medical field, medical devices and instruments should be measured with the help of measuring instruments to make that surgical implants and instruments are being produced with accurate dimensions to ensure the safety of patients and meet the medical standards. Innovations in Measuring Tools
The following innovations are taking place in measuring tools providing the analytical method to be used:
- Digital Integration. Measuring tools have digital display and some of them can output data. It makes measuring process to be more oriented and also reduces the risk of manual errors.
- Non-Contact Measurement. Some modern measuring tools are laser micrometers and vision systems. They can measure an item without touching it. This can be especially useful for measuring soft or delicate material. Permanent portable CMMs can be used for measuring parts of large sizes right on the shop floor.
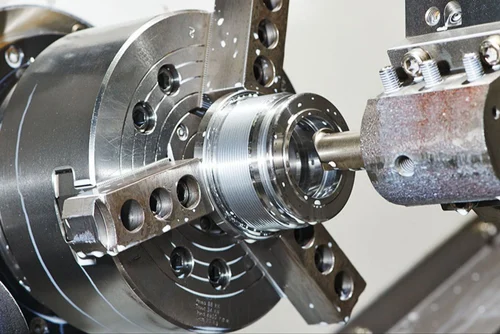
Coolant System
Coolant systems are an integral aspect of CNC machining that determines the optimal performance and life cycle of the tools and machines. It manages the heat produced during the cutting process, minimizes friction, and keeps the chips away from the cutting area. As a result, the coolant system plays a significant role in enhancing the surface finish quality and preventing the wear and deformation of the tool and workpiece, respectively. There are several types of coolant systems designed to meet various machining needs. Flood coolant systems expose the cutting area to a significant quantity of coolant, which is useful in heavy-duty manufacturing tasks. The machine tools are typically exposed to high speed and feed rates, and the machining operation generates high amounts of friction. The flood coolant system offers improved cooling and lubrication, optimizing the outcome. By contrast, mist coolant systems disperse fine some quantity of misted coolant and are suitable for high-speed machining of softer materials. It is essential to use mist systems when machining at lower speeds to minimize the amount of airborne particles and also to reduce the consumption of the coolant. Alternatively, through-spindle coolant systems disperse the coolant directly through the spindle and tool, linear cooling at the cutting edge. It is used in drilling deep holes and machining complex geometries, leading to prolonged tool life and superior composed part quality. Selecting the appropriate coolant depends on the material used and the machining process.
Different Types of Coolant Systems
- water-soluble coolants: they have a good cooling effect and can be used for practically all materials. They are the cheapest and the easiest to mix.
- synthetic coolants: they have the best lubricating properties, they are the most stable and ideal for high-speed machining. They are also not very prone to bacterial growth.
- semi-synthetic coolants: they offer a combination of water-soluble and synthetic coolants, being relatively good at lubricating and cooling.
- oil-based coolants: they have the best lubrication properties. They are used for tough materials or heavy work, but they are also more difficult to remove after being used on machines.
- real-world application: a medical device producer used synthetic coolants for CNC machining that was used for manufacturing titanium implants. The products had improved finishes and the process of production was 20% more efficient.
maintenance of coolant systems
There are several ways of maintaining a coolant system in one’s CNC machine, all of which ensure longer proper work of one’s machine:
-
Regular checking of coolant level, coolant concentration, and pH.
-
Using a refractometer to check concentration better.
-
Removal of chips along with the other materials from the coolant on a regular basis.
-
Installation of a filtering system to maintain cleanliness.
Replacing the coolant
The coolant used in CNC machines must be replaced on a semi-regular basis and once it is a proactive decision to replace the coolant at the beginning of a working day. Making the decision too late results in being forced to stop one’s machines during workdays, and leaving an existing coolant for too long can stop one’s production entirely.
Applications of coolant systems
There are a wide variety of industries and applications in which CNC machines are used because their materials are easy to work with and shape into diverse objects. Of such applications, one can list:
– Automotive for engine components.
– Aerospace for high-speed components.
– Medica for surgery instruments and implants.
– General manufacturing for a longer cutting tool life and a guaranteed higher part quality.
In the automotive industry, for example, coolant systems are essential for machining engine blocks and cylinder heads which ensures that they meet the required performance and durability. technological advances in coolant systems continue to improve their efficiency and impact to the environment such innovations include:
-
Advanced filtration systems which improve the efficiency of removing contaminants in the coolants thereby extending useful life of the coolants and reducing maintenance.
-
Eco-friendly coolants- technology has been developed to create non-toxic and bio-degradable coolants which have reduced the cost of disposal of coolants and their environmental impact.
-
Smart coolant systems which use IoT technology and sensors to monitor the condition of the coolant enabling the user to optimize their machining process and reduce downtime when the coolant needs to be changed.









